Date:2025-04-15 Categories:Product knowledge Hits:527 From:Guangdong Youfeng Microelectronics Co., Ltd
1. Zero Gate Bias (VGS = 0V):When VGS is zero, the PN junctions between the P-type gates and the N-channel are unbiased. A small depletion region forms at the junctions, allowing maximum current (IDSS) to flow from the drain (D) to the source (S) under a positive drain-source voltage (VDS).
2. Reverse Gate Bias (VGS < 0V):Applying a negative VGS reverse-biases the PN junctions, expanding the depletion regions into the N-channel. This reduces the effective cross-sectional area of the channel, increasing its resistance and limiting the drain current (ID). As VGS becomes more negative, the depletion regions eventually merge, fully "pinching off" the channel and cutting off ID. The voltage at which this occurs is called the pinch-off voltage (VP).
3. Saturation Region:For VDS values exceeding the pinch-off threshold, ID remains nearly constant despite increasing VDS, making the JFET ideal for amplifiers. In this region, ID is primarily controlled by VGS, following the equation: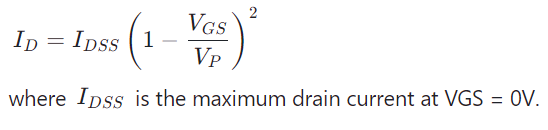
1. High Input Impedance: The reverse-biased PN junctions ensure negligible gate current (typically in the picoampere range), minimizing signal loading.
2. Voltage Control: Unlike bipolar transistors, JFETs rely on voltage (VGS) rather than current for operation, enabling precise signal regulation.
3. Low Noise: YFW’s JFETs are engineered for minimal noise, critical for audio preamps and high-frequency applications.
4. Temperature Stability: N-channel JFETs exhibit a negative temperature coefficient, reducing thermal runaway risks.
YFW’s N-channel JFETs excel in:
5. Audio Amplifiers: Their low noise and high input impedance preserve signal fidelity.
6. RF Circuits: Used in mixers and amplifiers due to high-frequency performance.
7. Voltage Regulators: As voltage-controlled resistors in feedback loops.
8. Switching Systems: For low-power digital logic and power management.
YFW’s N-channel JFETs leverage the field-effect principle to provide efficient, stable, and low-noise signal control. By modulating the channel width via VGS, these devices enable precise current regulation across various operating regions, making them indispensable in modern electronics. Whether in amplifiers, switches, or voltage regulators, YFW’s JFETs deliver reliability and performance tailored to demanding applications.

Previous: Classification, Structure, and Principle of MOSFET